
(As for the other four pins, ground is 0V, and the Uno board has a 3.3V supply for VCC, so these pins don't need a diode, and I hardwired /WP and /HOLD to 3.3V Vcc.) UPDATE: I forgot to add the 330 Ohm resistors in series with the output of the Uno drivers.
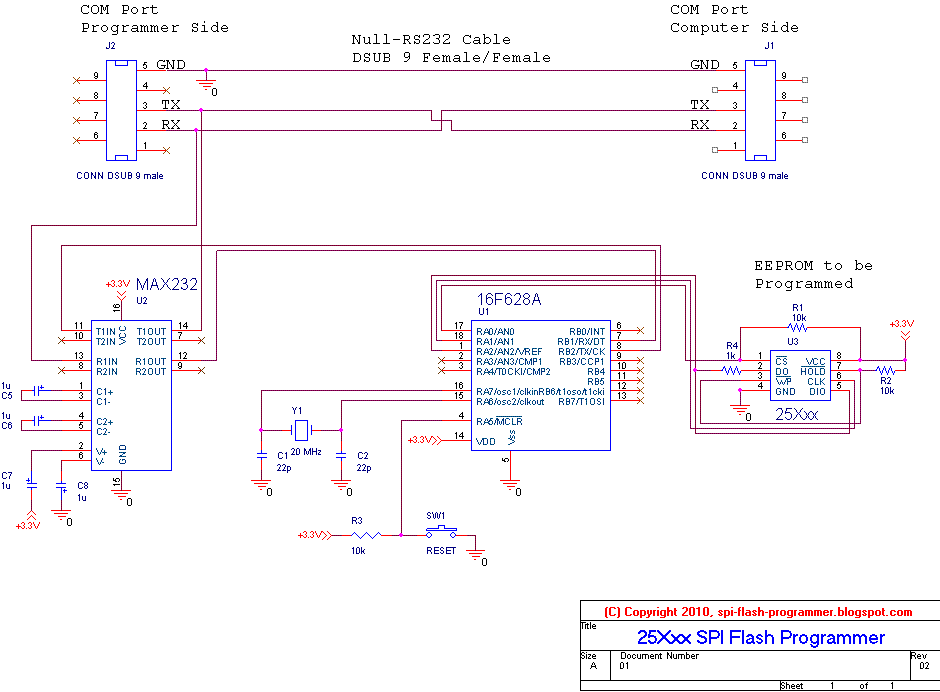
Note: 'High impedance' means you can ignore that signal (it is driven to not 0 or 1, but extremely high resistance, so it is effectively an open circuit). The bottom axis is time, the vertical axes represent four SPI pins and the sequence data should appear on them over time to execute an instruction. In the diagram for this section I copied the chip erase timing diagram from the datasheet because it is the easiest to understand. Each SPI device responds to its own set of instructions (e.g., a flash device will have a read or erase instruction) and the timing diagram is the link between the conceptual behavior of the instruction and the actual hardware protocol to execute that instruction. Timing diagrams explain the sequencing of the data across the pins to issue instructions to the device. Now that I've explained flash, SPI, and a specific implementation of an SPI flash device, the next things you need to understand are communication timing diagrams. Pin 8: VCC This is simply the source voltage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
